冗余连接问题(非常详细,图文并茂)
接触过数据结构的读者都知道,数据结构里囊括了很多种存储数据的方案,包括线性表、树、图等。线性表的特征非常明显,很容易辨识,树和图是初学者经常混淆的。
在数据结构中,所有的树都可以看做是图型结构,但反过来,只有「连通且不存在环路的无向图」可以看做是树型结构。例如,观察下方哪个是树型结构,哪个是图型结构?
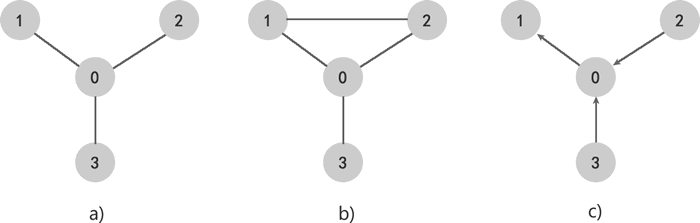
图 1 树和图的区别
图 1 中,c) 是有向图,无法被看做是树型结构。重点观察 a) 和 b),它们都是无向图,并且各自包含的顶点都是相互连通的,唯一的不同在于,b) 中存在 1-0-2-1 这条环路,而 a) 中不存在环路,因此 a) 既可以看做是一张图,也可以看做是一棵树;而 b) 只能看做是一张图。
本节要带领大家解决的冗余连接问题,指的是给定一张图型结构,它是由 n 个顶点的树外加一条边构成的,要求找出这条冗余的边。图中所有边的信息都记录在长度为 n 的二维数组 edges 里,edges[i] = [ai, bi] 表示图中在 ai 和 bi 之间存在一条边。如果有多条符合条件的边,则返回 edges 数组中最后出现的那个。
举个简单的例子,从下图中找到冗余的那条边。
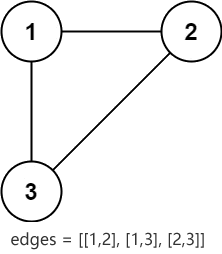
图 2 给定的图
观察图 2 不难发现,冗余的边可以是 [1, 2]、[1, 3]、[2, 3] 中的任意一条,删除它们中的一个,剩下的就是一棵树。当然多条符合条件的边时,题目要求返回 edges 数组中最后出现的那个,也就是 [2, 3] 这条边。
冗余连接问题可以用并查集解决,接下来给大家讲解具体的实现过程。
仍以图 2 为例,并查集解决冗余连接问题的过程是:
下面是用并查集解决冗余问题的 C 语言程序:
下面是用并查集解决冗余问题的 Java 程序:
下面是用并查集解决冗余问题的 Python 程序:
运行程序,输出结果为:
在数据结构中,所有的树都可以看做是图型结构,但反过来,只有「连通且不存在环路的无向图」可以看做是树型结构。例如,观察下方哪个是树型结构,哪个是图型结构?

图 1 树和图的区别
图 1 中,c) 是有向图,无法被看做是树型结构。重点观察 a) 和 b),它们都是无向图,并且各自包含的顶点都是相互连通的,唯一的不同在于,b) 中存在 1-0-2-1 这条环路,而 a) 中不存在环路,因此 a) 既可以看做是一张图,也可以看做是一棵树;而 b) 只能看做是一张图。
本节要带领大家解决的冗余连接问题,指的是给定一张图型结构,它是由 n 个顶点的树外加一条边构成的,要求找出这条冗余的边。图中所有边的信息都记录在长度为 n 的二维数组 edges 里,edges[i] = [ai, bi] 表示图中在 ai 和 bi 之间存在一条边。如果有多条符合条件的边,则返回 edges 数组中最后出现的那个。
举个简单的例子,从下图中找到冗余的那条边。

图 2 给定的图
观察图 2 不难发现,冗余的边可以是 [1, 2]、[1, 3]、[2, 3] 中的任意一条,删除它们中的一个,剩下的就是一棵树。当然多条符合条件的边时,题目要求返回 edges 数组中最后出现的那个,也就是 [2, 3] 这条边。
冗余连接问题可以用并查集解决,接下来给大家讲解具体的实现过程。
并查集解决冗余连接问题
并查集解决冗余连接问题的思路是,依次判断 edges 数组中存储的各个边是否是冗余的,判断依据是:如果当前边两端的顶点不属于一个集合,就将它们合并为一个集合;反之,如果当前边两端的顶点属于同一个集合,表明两个顶点先前已经连通过了,再添加当前边会导致出现环路,因此当前边就是冗余的。仍以图 2 为例,并查集解决冗余连接问题的过程是:
- 初始状态下,顶点 1、2、3 各自属于不同的集合;
- 检查 [1, 2] 边是否冗余:顶点 1 和 2 位于不同的集合里,因此 [1, 2] 不是冗余的,将顶点 1 和 2 合并为同一个集合;
- 检查 [1, 3] 边是否冗余:顶点 1 和 3 位于不同的集合里,因此 [1, 3] 不是冗余的,将顶点 1 和 3 合并为同一个集合;
- 检查 [2, 3] 边是否冗余:顶点 2 和 3 位于同一个集合里,因此 [2, 3] 是冗余的。
下面是用并查集解决冗余问题的 C 语言程序:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef enum { false, true } bool;
#define MAX_SIZE 1000 // 可以根据需要调整最大尺寸
// 并查集数组
typedef struct {
int parent[MAX_SIZE];
int count;
}UnionFind;
// 初始化并查集
void initialize(UnionFind* uf, int size) {
for (int i = 0; i <= size; i++) {
uf->parent[i] = i;
}
uf->count = size;
}
// 查找根节点(代表元素)
int find(UnionFind* uf, int x) {
if (uf->parent[x] != x) {
uf->parent[x] = find(uf, uf->parent[x]); // 路径压缩
}
return uf->parent[x];
}
// 合并两个元素所在的集合
void unionSets(UnionFind* uf, int x, int y) {
//找到两个元素所在集合的代表元素
int xRoot = find(uf, x);
int yRoot = find(uf, y);
//如果代表元素不同,表明它们是两个集合,将它们合并
if (xRoot != yRoot) {
uf->parent[xRoot] = yRoot; // uf->parent[yRoot] = xRoot;
uf->count--;
}
}
int* findRedundantConnection(int(*edgs)[2], int n) {
UnionFind uf;
initialize(&uf, n);
// 遍历所有的边
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
//判断当前边是否冗余
if (find(&uf, edgs[i][0]) == find(&uf, edgs[i][1])) {
return edgs[i];
}
else
{
unionSets(&uf, edgs[i][0], edgs[i][1]);
}
}
}
int main() {
int edgs[3][2] = { {1,2},{1,3},{2,3} };
//找到冗余的边
int * ret = findRedundantConnection(edgs, 3);
printf("冗余的边是:[%d, %d]\n", ret[0], ret[1]);
return 0;
}
下面是用并查集解决冗余问题的 Java 程序:
// 并查集类,用于处理集合合并和查找操作(在 UnionFind.java 文件中)
public class UnionFind {
private int[] parent; // 记录节点的父节点
private int count; // 记录集合的数量
// 构造函数,初始化并查集,每个节点的父节点初始为自己,集合数量为节点个数
public UnionFind(int size) {
parent = new int[size + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= size; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
count = size;
}
// 查找根节点(代表元素)的方法,同时进行路径压缩
public int find(int x) {
if (parent[x] != x) {
parent[x] = find(parent[x]); // 路径压缩
}
return parent[x];
}
// 合并两个元素所在的集合
public void unionSets(int x, int y) {
int xRoot = find(x);
int yRoot = find(y);
if (xRoot != yRoot) {
parent[xRoot] = yRoot; // 合并集合
count--;
}
}
// 获取当前集合的数量
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
}
// FindRedundantConnection 类定义(在 FindRedundantConnection.java 文件中)
public class FindRedundantConnection {
// 查找冗余连接的方法
public int[] findRedundantConnection(int[][] edges) {
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(edges.length);
int[] result = new int[2];
for (int[] edge : edges) {
if (uf.find(edge[0]) == uf.find(edge[1])) {
result[0] = edge[0];
result[1] = edge[1];
} else {
uf.unionSets(edge[0], edge[1]);
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] edges = { {1, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 3} };
FindRedundantConnection validPath = new FindRedundantConnection();
int[] result = validPath.findRedundantConnection(edges);
System.out.println("冗余的边是:[" + result[0] + ", " + result[1] + "]");
}
}
下面是用并查集解决冗余问题的 Python 程序:
class UnionFind:
def __init__(self, size):
self.parent = [i for i in range(size + 1)]
self.count = size
# 初始化并查集
def initialize(self, size):
for i in range(size + 1):
self.parent[i] = i
self.count = size
# 查找操作,返回元素所在集合的代表元素
def find(self, x):
if self.parent[x] != x:
self.parent[x] = self.find(self.parent[x]) # 路径压缩
return self.parent[x]
# 合并两个集合
def union_sets(self, x, y):
x_root = self.find(x)
y_root = self.find(y)
if x_root != y_root:
self.parent[x_root] = y_root
self.count -= 1
# 查找冗余连接的方法
def find_redundant_connection(edges):
uf = UnionFind(len(edges))
result = [0, 0]
for edge in edges:
if uf.find(edge[0]) == uf.find(edge[1]):
result[0], result[1] = edge[0], edge[1]
else:
uf.union_sets(edge[0], edge[1])
return result
if __name__ == "__main__":
edges = [[1, 2], [1, 3], [2, 3]]
ret = find_redundant_connection(edges)
print(f"冗余的边是:[{ret[0]}, {ret[1]}]")
运行程序,输出结果为:
冗余的边是:[2, 3]
 ICP备案:
ICP备案: 公安联网备案:
公安联网备案: