Spring Boot整合MyBatis过程详解(附带实例))
MyBatis 官方对 Spring Boot 提供了完善的支持,能够方便地将 MyBatis 集成到 Spring Boot 项目中。
接下来就让我们一步一步地将 MyBatis 集成到 Spring Boot 项目中,实现学生信息管理功能。
MyBatis-Spring-Boot-Starter 不是 Spring Boot 官方开发的启动器,它是一个集成包,对 MyBatis、MyBatis-Spring 和 Spring Boot 都存在依赖,需要注意三者的版本对应关系,如下表所示。
由于 MyBatis-Spring-Boot-Starter 是 MyBatis 官方提供的组件而非 Spring Boot 开发的,因此它的版本和 Spring Boot 不一样,使用时需要注意版本。
MyBatis 针对 Spring Boot 项目做了非常完善的支持,使用 MyBatis-Spring-Boot-Starter 组件可以做到以下几点:
MyBatis 的启动过程看起来很复杂,其实主要完成以下几个操作:
因此,使用 MyBatis-Spring-Boot-Starter启动器之后,只需要在配置文件中定义数据源,MyBatis 就会使用该数据源自动创建 SqlSessionFactoryBean 以及 SqlSessionTemplate,同时会自动扫描 Mappers 接口,并注册到 Spring 上下文中,相当于所有数据库的底层操作 MyBatis 都自动完成了。
MyBatis 对于 SQL 映射提供了两种解决方案,一种是简化后的 XML 配置版,另一种是使用注解解决一切问题。
下面将演示 Spring Boot 项目集成 MyBatis-spring-boot-starter 组件的过程,以便进一步构建数据库应用。
其实,也可以直接在 Mapper 类上添加注解 @Mapper,这样 Spring Boot 也会自动注入 Spring。不过,建议使用上面代码中使用的这种,不然给每个 Mapper 添加注解也挺麻烦。
接下来定义 MyBatis 的核心文件:mapper 映射文件。在 resources/mapper 目录创建 StudentMapper.xml 映射文件,具体实例代码如下:
单击 Run Test 或在方法上右击,选择 Run 'testSelectAll',运行测试方法,结果如下图所示。
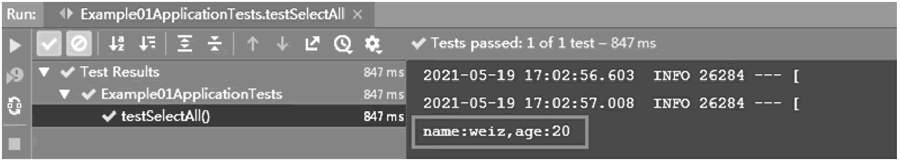
图 1 单元测试的运行结果
结果表明单元测试方法 testSelectAll() 运行成功,并输出了相应的学生数据查询结果。这说明在项目中成功集成 MyBatis,并成功执行了数据查询操作。
接下来就让我们一步一步地将 MyBatis 集成到 Spring Boot 项目中,实现学生信息管理功能。
MyBatis-Spring-Boot-Starter简介
MyBatis 官方为帮助开发者快速集成 Spring Boot 项目、构建基于 Spring Boot 的 MyBatis 应用程序,提供了针对 Spring Boot 的启动器:MyBatis-Spring-Boot-Starter。MyBatis-Spring-Boot-Starter 不是 Spring Boot 官方开发的启动器,它是一个集成包,对 MyBatis、MyBatis-Spring 和 Spring Boot 都存在依赖,需要注意三者的版本对应关系,如下表所示。
| MyBatis-Spring-Boot-Starter | MyBatis-Spring | Spring Boot | Java |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.1 | 2.0(需要 2.0.2,并支持所有功能) | 2.1 或更高 | 8 或更高 |
| 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.5 | 6 或更高 |
由于 MyBatis-Spring-Boot-Starter 是 MyBatis 官方提供的组件而非 Spring Boot 开发的,因此它的版本和 Spring Boot 不一样,使用时需要注意版本。
MyBatis 针对 Spring Boot 项目做了非常完善的支持,使用 MyBatis-Spring-Boot-Starter 组件可以做到以下几点:
- 构建独立的应用;
- 几乎可以零配置;
- 需要很少的 XML 配置。
MyBatis 的启动过程看起来很复杂,其实主要完成以下几个操作:
- 自动发现存在的数据源;
- 利用 SqlSessionFactoryBean 创建并注册 SqlSessionFactory;
- 创建并注册 SqlSessionTemplate;
- 自动扫描 Mappers,并注册到 Spring 上下文中,方便程序的注入使用。
因此,使用 MyBatis-Spring-Boot-Starter启动器之后,只需要在配置文件中定义数据源,MyBatis 就会使用该数据源自动创建 SqlSessionFactoryBean 以及 SqlSessionTemplate,同时会自动扫描 Mappers 接口,并注册到 Spring 上下文中,相当于所有数据库的底层操作 MyBatis 都自动完成了。
MyBatis 对于 SQL 映射提供了两种解决方案,一种是简化后的 XML 配置版,另一种是使用注解解决一切问题。
Spring Boot集成MyBatis
MyBatis 官方针对 Spring Boot 提供了启动包:MyBatis-spring-boot-starter组件,使得 Spring Boot 构建 MyBatis 应用程序更加简单方便。下面将演示 Spring Boot 项目集成 MyBatis-spring-boot-starter 组件的过程,以便进一步构建数据库应用。
1) 添加依赖
首先需要在 pom.xml 文件中引入 MyBatis-spring-boot-starter 依赖包:
<<dependency>
<groupId>org.MyBatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>MyBatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>>
在上面的示例中,引入 MyBatis-spring-boot-starter 组件需要指定版本号。另外,还需要引入 mysql-connector-java 连接驱动。2) 应用配置
在 application.properties 中添加 MyBatis 的相关配置:# mapper.xml配置文件的路径 MyBatis.mapper-locations=classpath:/mapper/*.xml MyBatis.type-aliases-package=com.weiz.example01.model # 数据库连接 spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/MyBatis_test?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=true spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=root spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver在上面的配置中,主要是数据库连接和 Mapper 文件相关的配置,具体配置说明如下:
- MyBatis.mapper-locations:配置 Mapper 对应的 XML 文件路径;
- MyBatis.type-aliases-package:配置项目中的实体类包路径;
- spring.datasource.*:数据源相关配置。
3) 修改启动类
在启动类中添加对 Mapper 包的扫描注解 @MapperScan,Spring Boot 启动时会自动加载包路径下的 Mapper。
@Spring BootApplication
@MapperScan("com.weiz.mapper")
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
在上面的示例中,使用 MapperScan 注解定义需要扫描的 Mapper 包。其实,也可以直接在 Mapper 类上添加注解 @Mapper,这样 Spring Boot 也会自动注入 Spring。不过,建议使用上面代码中使用的这种,不然给每个 Mapper 添加注解也挺麻烦。
4) 创建数据库和表
首先创建 mybatis_test 数据库,然后在数据库中创建 student 表,脚本如下:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS 'student';
CREATE TABLE 'student' (
'id' bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键id',
'name' varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名',
'sex' int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
'age' int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ('id')
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
5) 创建实体类
在 model 目录创建 Student 实体类,属性与创建的 Student 表中的字段一致,示例代码如下:
public class Student {
private Long id;
private String name;
private int sex;
private int age;
public Student(){
}
public Student(String name, int sex, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
}
//省略get、set方法
};
6) 添加mapper接口和映射文件
创建数据库表之后,接下来定义 mapper 接口。首先在 com.weiz.example01.mapper 包中创建 StudentMapper 接口,然后定义一个查询方法,具体代码如下:
public interface StudentMapper {
List<Student> selectAll();
}
在上面的示例中,定义了查询学生信息的 seletAll() 方法。需要注意的是,mapper 接口中的方法名需要和 XML 配置中的 id 属性一致,不然找不到方法去对应执行的 SQL。接下来定义 MyBatis 的核心文件:mapper 映射文件。在 resources/mapper 目录创建 StudentMapper.xml 映射文件,具体实例代码如下:
<<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//MyBatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://MyBatis.org/dtd/MyBatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.weiz.example01.mapper.StudentMapper" >
<select id="selectAll" resultMap="BaseResultMap" >
SELECT
*
FROM student
</select>
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.weiz.example01.model.Student" >
<id column="id" property="id" jdbcType="BIGINT" />
<result column="name" property="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="sex" property="sex" javaType="INTEGER"/>
<result column="age" property="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" />
</resultMap>
</mapper>>
在上面的示例中,通过 <select> 标签映射 mapper 接口中定义的 selectAll() 方法,标签的 id 为 mapper 接口中的方法,然后通过 <resultMap> 映射查询结果集字段与实体类 Student 的映射关系。7) 测试调用
创建单元测试类和测试方法 testSelectAll(),具体测试代码如下:
@Autowired
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Test
public void testSelectAll() {
// 查询
List<Student> students = studentMapper.selectAll();
for (Student stu : students){
System.out.println("name:"+stu.getName()+",age:"+stu.getAge());
}
}
上面是简单的使用 MyBatis 的测试示例,使用 @Autowired 将 StudentMapper 注入后即可直接调用。单击 Run Test 或在方法上右击,选择 Run 'testSelectAll',运行测试方法,结果如下图所示。

图 1 单元测试的运行结果
结果表明单元测试方法 testSelectAll() 运行成功,并输出了相应的学生数据查询结果。这说明在项目中成功集成 MyBatis,并成功执行了数据查询操作。
 ICP备案:
ICP备案: 公安联网备案:
公安联网备案: