ArkUI栅格布局(GridRow和GridCol)详解(附带实例)
栅格布局是一种通用的辅助定位工具,对移动设备的界面设计有较好的借鉴作用。其主要优势包括:
GridRow 为栅格容器组件,需要与栅格子组件 GridCol 在栅格布局场景中联合使用。
栅格系统默认断点将设备宽度分为 xs、sm、md、lg 四类,如下表所示。
在 GridRow 栅格组件中,允许开发者使用 breakpoints 自定义断点的取值范围,最多支持 6 个断点,除了默认的 4 个断点外,还可以启用 xl、xxl 两个断点,总共支持 6 种不同尺寸(xs, sm, md, lg, xl, xxl)设备的布局设置,如下表所示。
针对断点位置,开发者可以根据实际使用场景,通过一个单调递增数组来进行设置。由于 breakpoints 最多支持 6 个断点,因此单调递增数组的最大长度为 5。例如:
又如:
栅格系统通过监听窗口或容器的尺寸变化进行断点,通过 reference 设置断点切换参考物。考虑到应用可能以非全屏窗口的形式显示,因此以应用窗口宽度为参照物更为通用。
例如,使用栅格的默认列数(12 列),通过断点设置将应用宽度分成 6 个区间,在各区间中,每个栅格子元素占用的列数均不同,示例代码如下:
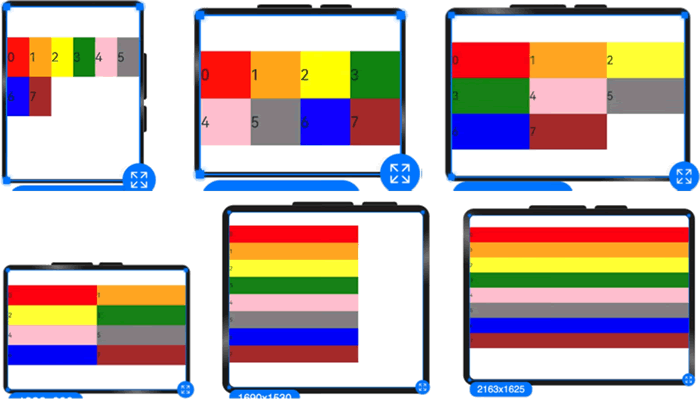
图 1 栅格容器布局显示效果
Columns 的默认值为 12,即在未设置 columns 时,任何断点下,栅格布局被分成 12 列,示例代码如下:
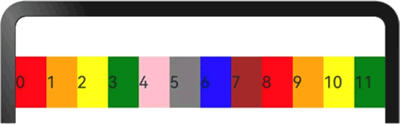
图 2 设置布局总列数后的显示效果
当 columns 为自定义值时,栅格布局在任何尺寸设备下都被分为 columns 列。在下面的实例中,分别设置栅格布局列数为 4 和 8,子元素默认占一列。
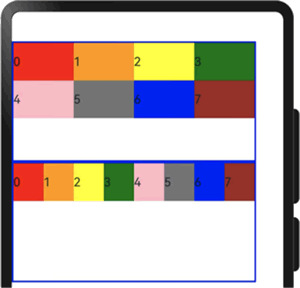
图 3 不同列数的显示效果对比
当 columns 类型为 GridRowColumnOption 时,支持 6 种不同尺寸(xs, sm, md, lg, xl, xxl)设备的总列数设置,各个尺寸下的数值可不同,示例代码如下:
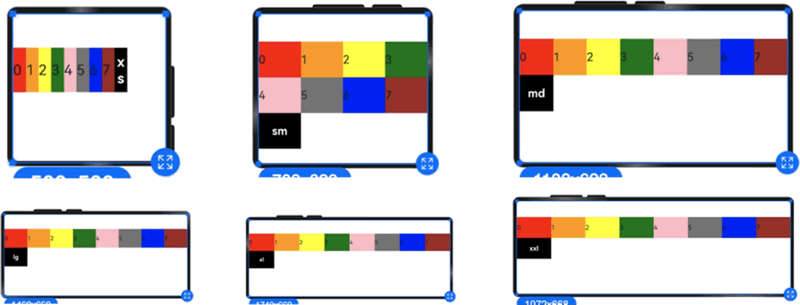
图 4 相同列数在不同尺寸下的显示效果
若只设置 sm 和 md 的栅格总列数,则较小的尺寸使用默认 columns 值(即 12),较大的尺寸使用前一个尺寸的 columns 值。这里只设置 sm:4 和 md:8,则较小尺寸的是 xs:12,较大尺寸的参照 md 的设置,为 lg:8, xl:8, xxl:8。
子组件默认从左往右排列,示例代码如下:
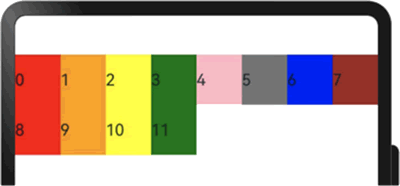
图 5 默认子组件排列方向显示效果
子组件从右往左排列的示例代码如下:
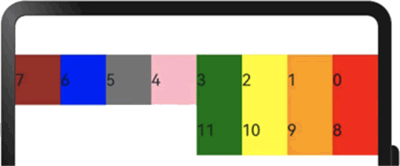
图 6 子组件从右向左排列的显示效果
例如,在下面的实例中,设置子组件在水平与垂直方向上与相邻元素的间距为 10:
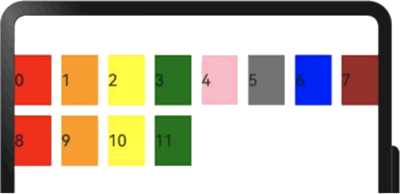
图 7 同时设置子组件间水平和垂直方向间距的显示效果
当 gutter 的类型为 GutterOption 时,可以单独设置栅格子组件的水平和垂直间距。此时,x 属性用于设置水平方向的间距,y 属性用于设置垂直方向的间距。示例代码如下:
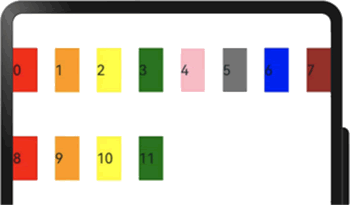
图 8 单独设置子组件间水平和垂直方向间距的显示效果
设置 span 的示例代码如下:

图 9 设置Span之后的显示效果
设置 offset 的示例代码如下:
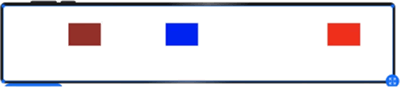
图 10 设置offset之后的显示效果
设置 order 的示例代码如下:

图 11 设置order之后的显示效果
示例代码如下:
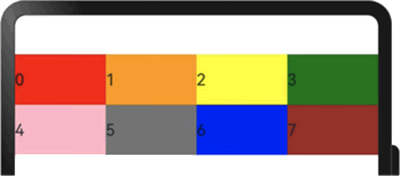
图 12 设置span之后的显示效果
当 span 类型为 GridColColumnOption 时,支持在 6 种不同尺寸(xs, sm, md, lg, xl, xxl)设备中设置子组件所占列数,并且各个尺寸下列数值可不同。示例代码如下:

图 13 不同尺寸下的显示效果
示例代码如下:
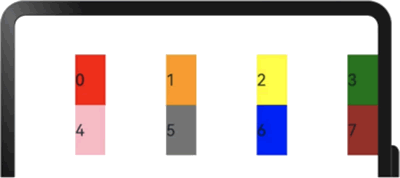
图 14 设置offset之后的显示效果
栅格默认分成 12 列,每一个子组件默认占 1 列,当偏移 2 列时,每个子组件及间距共占 3 列,因此一行放 4 个子组件。
当 offset 的类型为 GridColColumnOption 时,支持在 6 种不同尺寸(xs, sm, md, lg, xl, xxl)设备中设置子组件所占列数,并且各个尺寸下列数值可不同,示例代码如下:
图 15 子组件在不同断点处的偏移量
order 设置的示例代码如下:
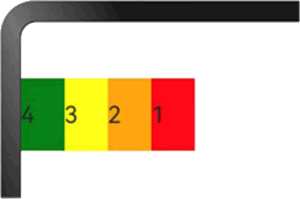
图 16 设置order之后的显示效果
当 order 类型为 GridColColumnOption 时,支持 6 种不同尺寸(xs, sm, md, lg, xl, xxl)设备中设置子组件排序次序。
例如,在 xs 设备中,子组件排列顺序为 1234;在 sm 设备中为 2341;在 md 子组件中排列顺序为 3412;在 lg 子组件中排列顺序为 2431,示例代码如下:
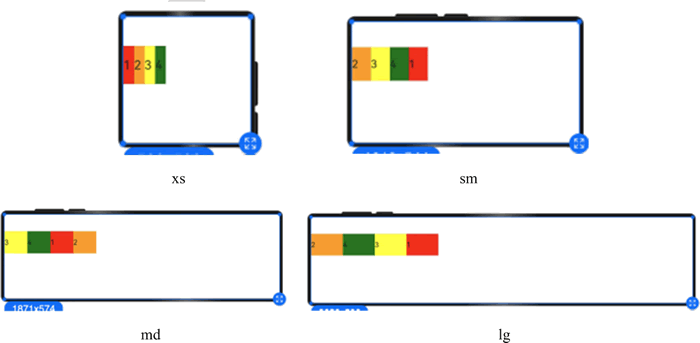
图 17 不同尺寸设备下不同order的显示效果
在下面实例中,栅格把整个空间分为 12 份;
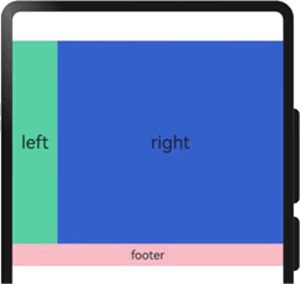
图 18 栅格组件的嵌套使用
综上所述,栅格组件提供了丰富的自定义能力,功能异常灵活和强大。只需明确栅格在不同断点下的 columns、margin、gutter 及 span 等参数,即可确定最终布局,而无须关心具体的设备类型及设备状态(如横竖屏)等。
- 提供可循的规律:栅格布局可以提供规律性的结构,解决了多尺寸多设备的动态布局问题。通过将页面划分为等宽的列和行,可以方便地对页面元素进行定位和排版;
- 统一的定位标注:栅格布局可以为系统提供统一的定位标注,保证不同设备上各个模块的布局一致性,从而减少设计和开发的复杂度,提高工作效率;
- 灵活的间距调整方法:栅格布局可以提供一种灵活的间距调整方法,满足特殊场景布局调整的需求。通过调整列与列和行与行的间距,可以控制整个页面的排版效果;
- 自动换行和自适应:栅格布局可以完成一对多布局的自动换行和自适应。当页面元素的数量超出了一行或一列的容量时,它们会自动换到下一行或下一列,并且在不同的设备上自适应排版,使得页面布局更加灵活,有更强的适应性。
GridRow 为栅格容器组件,需要与栅格子组件 GridCol 在栅格布局场景中联合使用。
栅格容器GridRow
栅格系统以设备的水平宽度(屏幕密度像素值,单位为 vp)作为断点依据,定义设备的宽度类型,形成了一套断点规则。开发者可根据需求在不同的断点区间实现不同的页面布局效果。栅格系统默认断点将设备宽度分为 xs、sm、md、lg 四类,如下表所示。
| 断点名称 | 取值范围(vp) | 设备描述 |
|---|---|---|
| xs | [0, 320] | 最小宽度类型设备 |
| sm | [320, 520] | 小宽度类型设备 |
| md | [520, 840] | 中等宽度类型设备 |
| lg | [840, +∞) | 大宽度类型设备 |
在 GridRow 栅格组件中,允许开发者使用 breakpoints 自定义断点的取值范围,最多支持 6 个断点,除了默认的 4 个断点外,还可以启用 xl、xxl 两个断点,总共支持 6 种不同尺寸(xs, sm, md, lg, xl, xxl)设备的布局设置,如下表所示。
| 断点名称 | 设备描述 |
|---|---|
| xs | 最小宽度类型设备 |
| sm | 小宽度类型设备 |
| md | 中等宽度类型设备 |
| lg | 大宽度类型设备 |
| xl | 特大宽度类型设备 |
| xxl | 超大宽度类型设备 |
针对断点位置,开发者可以根据实际使用场景,通过一个单调递增数组来进行设置。由于 breakpoints 最多支持 6 个断点,因此单调递增数组的最大长度为 5。例如:
breakpoints: {value: ['100vp', '200vp']}
表示启用 xs、sm、md 共 3 个断点,小于 100vp 的为 xs,100~200vp 的为 sm,大于 200vp 的为 md。又如:
breakpoints: {value: ['320vp', '520vp', '840vp', '1080vp']}
表示启用 xs、sm、md、lg、xl 共 5 个断点,小于 320vp 的为 xs,320~520vp 的为 sm,520~840vp 的为 md,840~1080vp 的为 lg,大于 1080vp 的为 xl。栅格系统通过监听窗口或容器的尺寸变化进行断点,通过 reference 设置断点切换参考物。考虑到应用可能以非全屏窗口的形式显示,因此以应用窗口宽度为参照物更为通用。
例如,使用栅格的默认列数(12 列),通过断点设置将应用宽度分成 6 个区间,在各区间中,每个栅格子元素占用的列数均不同,示例代码如下:
@Entry
@Component
struct GridLayoutDemo {
@State bgColors: Color[] = [
Color.Red, Color.Orange, Color.Yellow, Color.Green,
Color.Pink, Color.Grey, Color.Blue, Color.Brown
];
build() {
GridRow({
breakpoints: {
value: ['200vp', '300vp', '400vp', '500vp', '600vp'],
reference: BreakpointsReference.WindowSize
}
}) {
ForEach(this.bgColors, (color: Color, index?: number) => {
GridCol({
span: {
xs: 2, // 在最小宽度类型设备上,栅格子组件占据栅格容器 2 列
sm: 3, // 在小宽度类型设备上,栅格子组件占据栅格容器 3 列
md: 4, // 在中等宽度类型设备上,栅格子组件占据栅格容器 4 列
lg: 6, // 在大宽度类型设备上,栅格子组件占据栅格容器 6 列
xl: 8, // 在特大宽度类型设备上,栅格子组件占据栅格容器 8 列
xxl: 12 // 在超大宽度类型设备上,栅格子组件占据栅格容器 12 列
}
}) {
Row() {
Text(`${index}`)
}
.width('100%')
.height('50vp')
} .backgroundColor(color)
})
}
}
}
显示效果如下图所示:
图 1 栅格容器布局显示效果
布局的总列数
在 GridRow 中,通过 columns 设置栅格布局的总列数。Columns 的默认值为 12,即在未设置 columns 时,任何断点下,栅格布局被分成 12 列,示例代码如下:
@Entry
@Component
struct GridSample {
@State bgColors: Color[] = [
Color.Red, Color.Orange, Color.Yellow,
Color.Green, Color.Pink, Color.Grey,
Color.Blue, Color.Brown, Color.Red,
Color.Orange, Color.Yellow, Color.Green
];
build() {
// 栅格行组件
GridRow() {
// 通过循环渲染,向栅格行组件中添加栅格列子组件
ForEach(this.bgColors, (item: Color, index?: number) => {
GridCol() {
Row() {
Text(`${index}`)
}
.width('100%')
.height('50')
.backgroundColor(item)
}
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}
显示效果如下图所示:
图 2 设置布局总列数后的显示效果
当 columns 为自定义值时,栅格布局在任何尺寸设备下都被分为 columns 列。在下面的实例中,分别设置栅格布局列数为 4 和 8,子元素默认占一列。
import { promptAction } from '@kit.ArkUI';
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';
// 使用 Record 类型数据设置边框样式
let BorderWH: Record<string, Color | number> = { 'color': Color.Blue, 'width': 2 };
@Entry
@Component
struct GridSample {
@State bgColors: Color[] = [
Color.Red, Color.Orange, Color.Yellow,
Color.Green, Color.Pink, Color.Grey,
Color.Blue, Color.Brown
];
build() {
Column() {
Row() {
// 栅格行组件,设置一行显示 4 列
GridRow({ columns: 4 }) {
ForEach(this.bgColors, (item: Color, index?: number | underfined) => {
GridCol() {
Row() {
Text(`${index}`)
}
.width('100%')
.height('50')
}
.backgroundColor(item)
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
.height(160)
.border(BorderWH)
.width('90%')
Row() {
// 栅格行组件,设置一行显示 8 列
GridRow({ columns: 8 }) {
ForEach(this.bgColors, (item: Color, index?: number | undefined) => {
GridCol() {
Row() {
Text(`${index}`)
}
.width('100%')
.height('50')
}
.backgroundColor(item)
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
.height(160)
.border(BorderWH)
.width('90%')
}
}
}
显示效果如下图所示:
图 3 不同列数的显示效果对比
当 columns 类型为 GridRowColumnOption 时,支持 6 种不同尺寸(xs, sm, md, lg, xl, xxl)设备的总列数设置,各个尺寸下的数值可不同,示例代码如下:
import { promptAction } from '@kit.ArkUI';
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';
@Entry
@Component
struct GridSample {
@State bgColors: Color[] = [
Color.Red, Color.Orange, Color.Yellow,
Color.Green, Color.Pink, Color.Grey,
Color.Blue, Color.Brown
];
@State currentBreakpoint: string = 'unknown';
build() {
GridRow({
// 如果断点是 sm,每行显示 4 列;如果断点是 md,每行显示 8 列
columns: { sm: 4, md: 8 },
// 断点定义,5 个数字定义 6 个断点:xs, sm, md, lg, xl, xxl
breakpoints: { value: ['200vp', '300vp', '400vp', '500vp', '600vp'] }
}) {
ForEach(this.bgColors, (item: Color, index?: number) => {
GridCol() {
Row() {
Text(`${index}`)
}
.width('100%')
.height('50')
.backgroundColor(item)
}
})
GridCol() {
Row() {
Text(this.currentBreakpoint)
.fontColor(Color.White)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.backgroundColor(Color.Black)
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
}
.width('100%')
.height('50')
}
.onBreakpointChange((breakpoint: string) => {
this.currentBreakpoint = breakpoint;
})
}
}
}
显示效果如下图所示:
图 4 相同列数在不同尺寸下的显示效果
若只设置 sm 和 md 的栅格总列数,则较小的尺寸使用默认 columns 值(即 12),较大的尺寸使用前一个尺寸的 columns 值。这里只设置 sm:4 和 md:8,则较小尺寸的是 xs:12,较大尺寸的参照 md 的设置,为 lg:8, xl:8, xxl:8。
GridRow排列方向
栅格布局中,可以通过设置 GridRow 的 direction 属性来指定栅格子组件在栅格容器中的排列方向。该属性可以设置为 GridRowDirection.Row(从左往右排列)或 GridRowDirection.RowReverse(从右往左排列),以满足不同的布局需求。通过合理的 direction 属性设置,可以使得页面布局更加灵活和符合设计要求。子组件默认从左往右排列,示例代码如下:
@Entry
@Component
struct GridSample {
@State bgColors: Color[] = [
Color.Red, Color.Orange, Color.Yellow,
Color.Green, Color.Pink, Color.Grey,
Color.Blue, Color.Brown, Color.Red,
Color.Orange, Color.Yellow, Color.Green
];
build() {
// 子组件从左往右排列(默认值)
GridRow({ direction: GridRowDirection.Row, columns: 8 }) {
ForEach(this.bgColors, (item: Color, index?: number) => {
GridCol() {
Row() {
Text(`${index}`)
}
.width('100%')
.height('50')
}
.backgroundColor(item)
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}
显示效果如下图所示:
图 5 默认子组件排列方向显示效果
子组件从右往左排列的示例代码如下:
@Entry
@Component
struct GridSample {
@State bgColors: Color[] = [
Color.Red, Color.Orange, Color.Yellow,
Color.Green, Color.Pink, Color.Grey,
Color.Blue, Color.Brown, Color.Red,
Color.Orange, Color.Yellow, Color.Green
];
build() {
// 子组件从右往左排列
GridRow({ direction: GridRowDirection.RowReverse, columns: 8 }) {
ForEach(this.bgColors, (item: Color, index?: number) => {
GridCol() {
Row() {
Text(`${index}`)
}
.width('100%')
.height('50')
}
.backgroundColor(item)
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}
显示效果如下图所示:
图 6 子组件从右向左排列的显示效果
GridRow子组件间距
在 GridRow 中,可以通过 gutter 属性来设置子元素在水平和垂直方向的间距。当 gutter 的类型为 number 时,栅格子组件的水平和垂直方向的间距将被统一设置,且两者的间距值相等。例如,在下面的实例中,设置子组件在水平与垂直方向上与相邻元素的间距为 10:
@Entry
@Component
struct GridSample {
@State bgColors: Color[] = [
Color.Red, Color.Orange, Color.Yellow,
Color.Green, Color.Pink, Color.Grey,
Color.Blue, Color.Brown, Color.Red,
Color.Orange, Color.Yellow, Color.Green
];
build() {
// gutter 设置子组件在水平与垂直方向上与相邻元素的间距为 10 vp
GridRow({ gutter: 10, columns: 8 }) {
ForEach(this.bgColors, (item: Color, index?: number) => {
GridCol() {
Row() {
Text(`${index}`)
}
.width('100%')
.height('50')
}
.backgroundColor(item)
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}
显示效果如下图所示:
图 7 同时设置子组件间水平和垂直方向间距的显示效果
当 gutter 的类型为 GutterOption 时,可以单独设置栅格子组件的水平和垂直间距。此时,x 属性用于设置水平方向的间距,y 属性用于设置垂直方向的间距。示例代码如下:
@Entry
@Component
struct GridSample {
@State bgColors: Color[] = [
Color.Red, Color.Orange, Color.Yellow,
Color.Green, Color.Pink, Color.Grey,
Color.Blue, Color.Brown, Color.Red,
Color.Orange, Color.Yellow, Color.Green
];
build() {
// gutter 设置子组件水平方向的间距为 20 vp,垂直方向的间距为 50 vp
GridRow({ gutter: { x: 20, y: 50 }, columns: 8 }) {
ForEach(this.bgColors, (item: Color, index?: number) => {
GridCol() {
Row() {
Text(`${index}`)
}
.width('100%')
.height('50')
}
.backgroundColor(item)
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}
显示效果如下图所示:
图 8 单独设置子组件间水平和垂直方向间距的显示效果
子组件GridCol
GridCol 是 GridRow 组件的子组件,可以通过给 GridCol 传参或者设置属性这两种方式,设置 span(占用列数)、offset(偏移列数)和 order(元素序号)的值。设置 span 的示例代码如下:
// 以 Record 类型数据的方式设置布局参数
// 当断点是 xs 时组件占据 1 个单元格,当断点是 sm 时组件占据 2 个单元格
// 当断点是 md 时组件占据 3 个单元格,当断点是 lg 时组件占据 4 个单元格
let Gspan: Record<string, number> = {
xs: 1, sm: 2, md: 3, lg: 4
};
@Entry
@Component
struct GridSample {
build() {
Column() {
GridRow() {
// 组件占据 2 个单元格
GridCol({ span: 2 })
.backgroundColor(Color.Green)
.height(50)
// 当断点是 xs/sm/md/lg 时分别占据 1/2/3/4 个单元格
GridCol({ span: { xs: 1, sm: 2, md: 3, lg: 4 } })
.backgroundColor(Color.Blue)
.height(50)
// 通过属性的方式设置组件占据 2 个单元格
GridCol()
.span(2)
.backgroundColor(Color.Red)
.height(50)
// 通过 Record 形式,在不同断点下占据不同单元格
GridCol()
.span(Gspan)
.backgroundColor(Color.Yellow)
.height(50)
}
}
}
}
显示效果如下图所示:
图 9 设置Span之后的显示效果
设置 offset 的示例代码如下:
// 以 Record 类型数据的形式设置布局参数
// 当断点是 xs 时偏移量为 1 个单元格,当断点是 sm 时偏移量为 2 个单元格
// 当断点是 md 时偏移量为 3 个单元格,当断点是 lg 时偏移量为 4 个单元格
let Goffset: Record<string, number> = {
xs: 1, sm: 2, md: 3, lg: 4
};
@Entry
@Component
struct GridSample {
build() {
GridRow() {
// 设置单元格偏移量为 2 个单元格
GridCol({ offset: 2 })
.backgroundColor(Color.Brown)
.height(50)
// 当断点是 xs / sm / md / lg 时偏移量均为 2 个单元格
GridCol({ offset: { xs: 2, sm: 2, md: 2, lg: 2 } })
.backgroundColor(Color.Blue)
.height(50)
// 通过 Record 类型数据设置属性,在不同断点下使用不同偏移量
GridCol()
.offset(Goffset)
.backgroundColor(Color.Red)
.height(50)
}
.height('100%')
.width('100%')
}
}
显示效果如下图所示:
图 10 设置offset之后的显示效果
设置 order 的示例代码如下:
// 以 Record 类型数据的方式设置布局参数
// 当断点是 xs 时次序为 1,当断点是 sm 时次序为 2,
// 当断点是 md 时次序为 3,当断点是 lg 时次序为 4
let Gorder: Record<string, number> = {
xs: 1, sm: 2, md: 3, lg: 4
};
@Entry
@Component
struct GridSample {
build() {
GridRow({ columns: 4 }) {
// 设置排列次序为 2
GridCol({ order: 2 }) {
Text('1')
.height('100%')
.width('100%')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.fontColor(Color.White)
}
.backgroundColor(Color.Orange)
// 断点:xs→1, sm→2, md→3, lg→4
GridCol({ order: { xs: 1, sm: 2, md: 3, lg: 4 } }) {
Text('2')
.fontColor(Color.Yellow)
.height('100%')
.width('100%')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
}
.backgroundColor(Color.Brown)
// 以属性的方式设置次序为 2
GridCol() {
Text('3')
.fontColor(Color.Yellow)
.height('100%')
.width('100%')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
}
.backgroundColor(Color.Green)
.order(2)
// 以属性的方式设置不同断点下的次序
GridCol() {
Text('4')
.fontColor(Color.Yellow)
.height('100%')
.width('100%')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
}
.backgroundColor(Color.Blue)
.order(Gorder)
}
.height(100)
}
}
显示效果如下图所示:
图 11 设置order之后的显示效果
GridCol span
span 是子组件占栅格布局的列数,决定了子组件的宽度,其默认值为 1。当其类型为 number 时,子组件在所有尺寸设备下占用的列数相同。示例代码如下:
@Entry
@Component
struct GridSample {
@State bgColors: Color[] = [
Color.Red, Color.Orange, Color.Yellow,
Color.Green, Color.Pink, Color.Grey,
Color.Blue, Color.Brown
];
build() {
// 设置每行分配 8 个单元格
GridRow({ columns: 8 }) {
ForEach(this.bgColors, (color: Color, index?: number) => {
// 设置子组件占据的单元格个数为 2
GridCol({ span: 2 }) {
Row() {
Text(`${index}`)
}
.width('100%')
.height('50vp')
.backgroundColor(color)
}
})
}
}
}
显示效果如下图所示:
图 12 设置span之后的显示效果
当 span 类型为 GridColColumnOption 时,支持在 6 种不同尺寸(xs, sm, md, lg, xl, xxl)设备中设置子组件所占列数,并且各个尺寸下列数值可不同。示例代码如下:
@Entry
@Component
struct GridSample {
@State bgColors: Color[] = [
Color.Red, Color.Orange, Color.Yellow,
Color.Green, Color.Pink, Color.Grey,
Color.Blue, Color.Brown
];
build() {
// 设置每行分配 8 个单元格
GridRow({ columns: 8 }) {
ForEach(this.bgColors, (color: Color, index?: number) => {
// 设置子组件占据的单元格数量:
// 当断点为 xs 时占据 1 个单元格,
// 当断点为 sm 时占据 2 个单元格,
// 当断点为 md 时占据 3 个单元格,
// 当断点为 lg 时占据 4 个单元格
GridCol({ span: { xs: 1, sm: 2, md: 3, lg: 4 } }) {
Row() {
Text(`${index}`)
}
.width('100%')
.height('50vp')
} .backgroundColor(color)
})
}
}
}
显示效果如下图所示:
图 13 不同尺寸下的显示效果
GridCol offset
offset 表示栅格子组件相对于前一个子组件的偏移列数,默认值为 0。当 offset 类型为 number 时,所有子组件偏移相同列数。示例代码如下:
@Entry
@Component
struct GridSample {
@State bgColors: Color[] = [
Color.Red, Color.Orange, Color.Yellow,
Color.Green, Color.Pink, Color.Grey,
Color.Blue, Color.Brown
];
build() {
GridRow() {
ForEach(this.bgColors, (color: Color, index?: number) => {
// 设置子组件偏移量为 2 个单元格
GridCol({ offset: 2 }) {
Row() {
Text(`${index}`)
}
.width('100%')
.height('50vp')
} .backgroundColor(color)
})
}
}
}
显示效果如下图所示:
图 14 设置offset之后的显示效果
栅格默认分成 12 列,每一个子组件默认占 1 列,当偏移 2 列时,每个子组件及间距共占 3 列,因此一行放 4 个子组件。
当 offset 的类型为 GridColColumnOption 时,支持在 6 种不同尺寸(xs, sm, md, lg, xl, xxl)设备中设置子组件所占列数,并且各个尺寸下列数值可不同,示例代码如下:
@Entry
@Component
struct GridSample {
@State bgColors: Color[] = [
Color.Red, Color.Orange, Color.Yellow,
Color.Green, Color.Pink, Color.Grey,
Color.Blue, Color.Brown
];
build() {
GridRow() {
ForEach(this.bgColors, (color: Color, index?: number) => {
// 设置子组件在不同断点时的偏移量:
// xs 偏移 1 个单元格,sm 偏移 2 个单元格,
// md 偏移 3 个单元格,lg 偏移 4 个单元格
GridCol({ offset: { xs: 1, sm: 2, md: 3, lg: 4 } }) {
Row() {
Text('' + index)
}
.width('100%')
.height('50vp')
} .backgroundColor(color)
})
}
}
}
显示效果如下图所示:
图 15 子组件在不同断点处的偏移量
GridCol order
order 表示栅格子组件的序号,决定了子组件的排列次序:- 当子组件不设置 order 或者设置相同的 order 时,子组件按照代码顺序展示;
- 当子组件设置不同的 order 时,order 较小的组件在前,较大的在后;
- 当子组件部分设置 order,部分不设置 order 时,未设置 order 的子组件依次排序靠前,设置了 order 的子组件按照数值从小到大排列;
- 当 order 类型为 number 时,子组件在任何尺寸下排序次序一致。
order 设置的示例代码如下:
@Entry
@Component
struct GridSample {
build() {
GridRow() {
// 设置次序为 4
GridCol({ order: 4 }) {
Row() {
Text('1')
}
.width('100%')
.height('50vp')
} .backgroundColor(Color.Red)
// 设置次序为 3
GridCol({ order: 3 }) {
Row() {
Text('2')
}
.width('100%')
.height('50vp')
} .backgroundColor(Color.Orange)
// 设置次序为 2
GridCol({ order: 2 }) {
Row() {
Text('3')
}
.width('100%')
.height('50vp')
} .backgroundColor(Color.Yellow)
// 设置次序为 1
GridCol({ order: 1 }) {
Row() {
Text('4')
}
.width('100%')
.height('50vp')
} .backgroundColor(Color.Green)
}
}
}
显示效果如下图所示:
图 16 设置order之后的显示效果
当 order 类型为 GridColColumnOption 时,支持 6 种不同尺寸(xs, sm, md, lg, xl, xxl)设备中设置子组件排序次序。
例如,在 xs 设备中,子组件排列顺序为 1234;在 sm 设备中为 2341;在 md 子组件中排列顺序为 3412;在 lg 子组件中排列顺序为 2431,示例代码如下:
@Entry
@Component
struct GridSample {
build() {
GridRow() {
// 当处于断点 xs 时次序为 1,当处于断点 sm 时次序为 5,
// 当处于断点 md 时次序为 3,当处于断点 lg 时次序为 7
GridCol({ order: { xs: 1, sm: 5, md: 3, lg: 7 } }) {
Row() {
Text('1')
}
.width('100%')
.height('50vp')
} .backgroundColor(Color.Red)
// xs:2, sm:2, md:6, lg:1
GridCol({ order: { xs: 2, sm: 2, md: 6, lg: 1 } }) {
Row() {
Text('2')
}
.width('100%')
.height('50vp')
} .backgroundColor(Color.Orange)
// xs:3, sm:3, md:1, lg:6
GridCol({ order: { xs: 3, sm: 3, md: 1, lg: 6 } }) {
Row() {
Text('3')
}
.width('100%')
.height('50vp')
} .backgroundColor(Color.Yellow)
// xs:4, sm:4, md:2, lg:5
GridCol({ order: { xs: 4, sm: 4, md: 2, lg: 5 } }) {
Row() {
Text('4')
}
.width('100%')
.height('50vp')
} .backgroundColor(Color.Green)
}
}
}
显示效果如下图所示:
图 17 不同尺寸设备下不同order的显示效果
栅格组件的嵌套使用
栅格组件也可以嵌套使用,完成一些复杂的布局。在下面实例中,栅格把整个空间分为 12 份;
- 第一层 GridRow 嵌套 GridCol,分为中间大区域以及 footer 区域;
- 第二层 GridRow 嵌套 GridCol,分为 left 和 right 区域;
- 子组件的空间按照上一层父组件的空间划分。
@Entry
@Component
struct GridRowExample {
build() {
GridRow() {
// 这是一个容器组件,用于创建一个栅格行
GridCol({ span: { sm: 12 } }) {
// 在小屏幕设备上(sm)该列将占用 12 个单元格(意味着整行的宽度)
GridRow() {
// 第一个子列占用 2 个单元格
GridCol({ span: { sm: 2 } }) {
Row() {
Text('left').fontSize(24)
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.height('90%')
}
.backgroundColor('#ff41dbaa')
// 第二个子列占用 10 个单元格
GridCol({ span: { sm: 10 } }) {
Row() {
Text('right').fontSize(24)
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.height('90%')
}
.backgroundColor('#ff4168db')
}
.backgroundColor('#19000000')
}
// 第二个栅格列占用 12 个单元格,容纳一个显示“footer”的文本
GridCol({ span: { sm: 12 } }) {
Row() {
Text('footer')
.width('100%')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
}
.width('100%')
.height('10%')
.backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
}
}
.width('100%')
.height(300)
}
}
显示效果如下图所示:
图 18 栅格组件的嵌套使用
综上所述,栅格组件提供了丰富的自定义能力,功能异常灵活和强大。只需明确栅格在不同断点下的 columns、margin、gutter 及 span 等参数,即可确定最终布局,而无须关心具体的设备类型及设备状态(如横竖屏)等。
 ICP备案:
ICP备案: 公安联网备案:
公安联网备案: