Java Map接口用法详解
Map 接口的定义为:
public interface Map<K, V>{}
Map 接口定义时使用了泛型,并且定义了两个泛型 K 和 V,K 表示 key,规定了键元素的数据类型,V 表示 value,规定了值元素的数据类型,Map 接口中的方法如下表所示。| 方 法 | 描 述 |
|---|---|
| int size() | 获取集合长度 |
| boolean isEmpty() | 判断集合是否为空 |
| boolean containsKey(Object key) | 判断集合中是否存在某个 key 值 |
| boolean containsValue(Object value) | 判断集合中是否存在某个 value 值 |
| V get(Object key) | 取出集合中 key 对应的 value 值 |
| v put(K key, V value) | 向集合中存入一组 key-value 的元素 |
| V remove(Object key) | 删除集合中 key 对应的 value 值 |
| void putAII(Map<? extends K, ? extends V>m) | 向集合中添加另外一个 Map 集合 |
| void clear() | 清除集合中的所有元素 |
| Set<K> keySet() | 取出集合中所有的 key,返回一个 Set 集合 |
| Collection<V> values() | 取出集合中所有的 value,返回一个 Collection 集合 |
| Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet() | 将 Map 对象转换为 Set 对象 |
| int hashCode() | 获取集合的散列值 |
| boolean equals(Object o) | 比较两个集合是否相等 |
Map接口的实现类
Map 是一个接口,在实际开发中需要使用 Map 必须通过其实现类来完成实例化操作,Map 接口常用的实现类如下所示:- HashMap:存储一组无序,key 不可重复,但 value 可重复的元素。
- Hashtable:存储一组无序,key 不可重复,但 value 可重复的元素。
- TreeMap:存储一组有序,key 不可重复,但 value 可重复的元素,可以按照 key 来排序。
HashMap 是 Map 接口的一个常用实现类,定义如下所示:
public class HashMap<K, V> extends AbstractMap<K, V> implements Map<K, V> Cloneable, Serializable{}
下面的程序演示了 HashMap 的用法。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,String> hashMap = new HashMap<String,String> ();
hashMap.put("h", "Hello");
hashMap.put("w", "World");
hashMap.put("j", "Java");
hashMap.put("s", "JavaSE");
hashMap.put("m", "JavaME");
hashMap.put("e", "JavaEE");
System.out.println(hashMap);
hashMap.remove("e");
System.out.println("删除之后:"+hashMap);
hashMap.put("m", "Model");
System.out.println("添加之后:"+hashMap);
if(hashMap.containsKey("a")) {
System.out.println("集合中存在值为a的key");
}else {
System.out.println("集合中不存在值为a的key");
}
if(hashMap.containsValue("Java")) {
System.out.println("集合中存在值为Java的value");
}else {
System.out.println("集合中不存在值为Java的value");
}
Set keys = hashMap.keySet();
Iterator keysIterator = keys.iterator();
System.out.print("集合中的key:");
while(keysIterator.hasNext()) {
String key = (String) keysIterator.next();
System.out.print(key+",");
}
Collection values = hashMap.values();
Iterator valuesIterator = values.iterator();
System.out.print("集合中的value:");
while(valuesIterator.hasNext()) {
String value = (String) valuesIterator.next();
System.out.print(value+",");
}
System.out.print("key-value:");
keysIterator = keys.iterator();
while(keysIterator.hasNext()) {
String key = (String) keysIterator.next();
String value = hashMap.get(key);
System.out.print(key+"-"+value+",");
}
}
}
运行结果为:
{h=Hello, w=World, j=Java, s=JavaSE, m=JavaME, e=JavaEE}
删除之后:{h=Hello, w=World, j=Java, s=JavaSE, m=JavaME}
添加之后:{h=Hello, w=World, j=Java, s=JavaSE, m=Model}
集合中不存在值为a的key
集合中存在值为Java的value
集合中的key:h,w,j,s,m,
集合中的value:Hello,World,Java,JavaSE,Model,
key-value:h-Hello,w-World,j-Java,s-JavaSE,m-Model,
Hashtable 是较早推出的一个实现类,与 HashMap 的区别是:Hashtable 是线程安全的,但是性能较低;HashMap 是非线程安全的,但是性能较高。
从实际开发角度来讲,HashMap 使用的频率更高,Hashtable 的定义如下:
public class Hashtab<K, V> extends Dictionary<K, V> implements Map<K, V> Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{}
下面的实例演示了 Hashtable 的用法。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hashtable<String,String> hashtable = new Hashtable<String,String> ();
hashtable.put("h", "Hello");
hashtable.put("w", "World");
hashtable.put("j", "Java");
hashtable.put("s", "JavaSE");
hashtable.put("m", "JavaME");
hashtable.put("e", "JavaEE");
System.out.println(hashtable);
hashtable.remove("e");
System.out.println("删除之后:"+hashtable);
hashtable.put("m", "Model");
System.out.println("添加之后:"+hashtable);
if(hashtable.containsKey("a")) {
System.out.println("集合中存在值为a的key");
}else {
System.out.println("集合中不存在值为a的key");
}
if(hashtable.containsValue("Java")) {
System.out.println("集合中存在值为Java的value");
}else {
System.out.println("集合中不存在值为Java的value");
}
Set keys = hashtable.keySet();
Iterator keysIterator = keys.iterator();
System.out.print("集合中的key:");
while(keysIterator.hasNext()) {
String key = (String) keysIterator.next();
System.out.print(key+",");
}
Collection values = hashtable.values();
Iterator valuesIterator = values.iterator();
System.out.print("集合中的value:");
while(valuesIterator.hasNext()) {
String value = (String) valuesIterator.next();
System.out.print(value+",");
}
System.out.print("key-value:");
keysIterator = keys.iterator();
while(keysIterator.hasNext()) {
String key = (String) keysIterator.next();
String value = hashtable.get(key);
System.out.print(key+"-"+value+",");
}
}
}
运行结果为:
{h=Hello, w=World, j=Java, s=JavaSE, m=JavaME, e=JavaEE}
删除之后:{h=Hello, w=World, j=Java, s=JavaSE, m=JavaME}
添加之后:{h=Hello, w=World, j=Java, s=JavaSE, m=Model}
集合中不存在值为a的key
集合中不存在值为Java的value
集合中的key:h,w,j,s,m,
集合中的value:Hello,World,Java,JavaSE,Model,
key-value:h-Hello,w-World,j-Java,s-JavaSE,m-Model,
public class TreeMap<K, V> extends AbstractMap<K, V> implements NavigableMap<K, V> Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{}
下面的实例演示了 TreeMap 的用法。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<Integer,String> treeMap = new TreeMap<Integer,String>();
treeMap.put(3, "Java");
treeMap.put(5, "JavaME");
treeMap.put(1, "Hello");
treeMap.put(6, "JavaEE");
treeMap.put(2, "World");
treeMap.put(4, "JavaSE");
Set keys = treeMap.keySet();
Iterator keysIterator = keys.iterator();
while(keysIterator.hasNext()) {
Integer key = (Integer) keysIterator.next();
String value = treeMap.get(key);
System.out.print(key+"-"+value+",");
}
}
}
运行结果为:
1-Hello,2-World,3-Java,4-JavaSE,5-JavaME,6-JavaEE,
可以看到,无论向集合中保存数据时的顺序如何,TreeMap 内部会自动按照 key 升序对数据进行排序。此时的 key 是 Integer 类型的,那如果 key 不是一个可自动排序的数据类型,如自定义的 User 类型,TreeMap 能否对其进行排序呢?观察下面的实例程序:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<User,String> treeMap = new TreeMap<User,String>();
treeMap.put(new User(3,"Java"), "Java");
treeMap.put(new User(5,"JavaME"), "JavaME");
treeMap.put(new User(1,"Hello"), "Hello");
treeMap.put(new User(6,"JavaEE"), "JavaEE");
treeMap.put(new User(2,"World"), "World");
treeMap.put(new User(4,"JavaSE"), "JavaSE");
Set keys = treeMap.keySet();
Iterator keysIterator = keys.iterator();
while(keysIterator.hasNext()) {
User key = (User) keysIterator.next();
String value = treeMap.get(key);
System.out.println(key+"-"+value);
}
System.out.println("集合中第一个Entry:"+treeMap.firstEntry());
System.out.println("集合中第一个key:"+treeMap.firstKey());
System.out.println("集合中最后一个Entry:"+treeMap.lastEntry());
System.out.println("集合中最后一个key:"+treeMap.lastKey());
System.out.println("集合中比new User(3,Java)大的最小key值:"+treeMap.higherKey (new User(3,"Java")));
System.out.println("集合中比new User(3,Java)小的最大key值:"+treeMap.lowerKey(new User(3,"Java")));
System.out.println("集合中比new User(3,Java)大的最小的key-value对:"+treeMap. higherEntry(new User(3,"Java")));
System.out.println("集合中比new User(3,Java)小的最大的key-value对:"+treeMap. lowerEntry(new User(3,"Java")));
System.out.println("截取之后的集合:"+treeMap.subMap(new User(3,"Java") , new User(5,"JavaME")));
}
}
class User{
private int id;
private String name;
//getter、setter、有参构造函数、重写toString
}
运行结果如下图所示。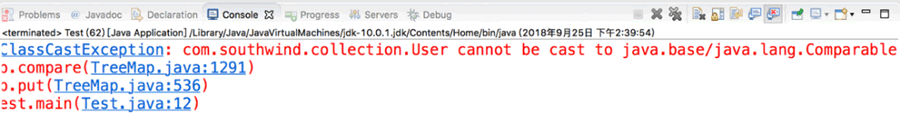
程序运行报错,错误原因是 User 的实例化对象无法进行排序,解决方法是让 User 类实现 Comparable 接口,并在 compareTo() 方法中实现对象的排序规则,代码如下:
class User implements Comparable{
……
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
/**
* A.compareTo(B)
* 返回值:
* 1表示A大于B
* 0表示A等于B
* -1表示A小于B
*/
User user = (User) o;
if(this.id > user.id) {
return 1;
}else if(this.id == user.id) {
return 0;
}else {
return -1;
}
}
}
再次运行程序,结果为:
User{id=1, name='Hello'}-Hello
User{id=2, name='World'}-World
User{id=3, name='Java'}-Java
User{id=4, name='JavaSE'}-JavaSE
User{id=5, name='JavaME'}-JavaME
User{id=6, name='JavaEE'}-JavaEE
集合中第一个Entry:User{id=1, name='Hello'}-Hello
集合中第一个key:User{id=1, name='Hello'}
集合中最后一个Entry:User{id=6, name='JavaEE'}-JavaEE
集合中最后一个key:User{id=6, name='JavaEE'}
集合中比new User(3,Java)大的最小key值:User{id=4, name='JavaSE'}
集合中比new User(3,Java)小的最大key值:User{id=2, name='World'}
集合中比new User(3,Java)大的最小的key-value对:User{id=4, name='JavaSE'}-JavaSE
集合中比new User(3,Java)小的最大的key-value对:User{id=2, name='World'}-World
截取之后的集合:{User{id=3, name='Java'}=Java, User{id=4, name='JavaSE'}=JavaSE}
 ICP备案:
ICP备案: 公安联网备案:
公安联网备案: