Q-learning算法详解(Python实现)
Q-learning 算法是强化学习中的一种基于价值(values-based)的算法,最终会学习出一个表格(Q-table),例如在一个游戏中有下面 5 种状态和 4 种动作,则表格如下图所示:
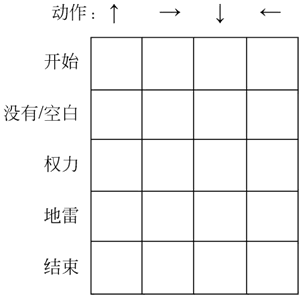
图 1 Q-table
表格的每一行代表每个状态,每一列代表每个动作,表格的数值就是在各个状态下采取各个动作时获得的最大的未来期望奖励。通过 Q-table 就可以找到每个状态下的最优行为,通过找到所有最优的动作得到最大的期望奖励。
因此计算表格的数值步骤为:
1) Q-table 初始化为 0。
2) 根据当前的 Q-table 给当前状态选择一个动作并执行。执行过程是一直到本轮训练停止才算完成。所谓 ε 贪婪策略是指开始时通过设置一个较大的 ε,让智能体探索环境并随机选择动作。随着智能体对环境的了解,降低 ε,这样智能体开始利用环境做出动作。
当某状态下选择了某个动作后,就可以用 Bellman 方程计算 Q 值:
3) 评估:采取动作得到了奖励后就可以用 Q 函数更新 Q(s, a),新 Q(s, a)=Q(s, a)+α[R(s, a)+γmaxQ′(s′, a′)-Q(s,a)]
【实例】利用 Python 实现 Q-learning 算法。

图 1 Q-table
表格的每一行代表每个状态,每一列代表每个动作,表格的数值就是在各个状态下采取各个动作时获得的最大的未来期望奖励。通过 Q-table 就可以找到每个状态下的最优行为,通过找到所有最优的动作得到最大的期望奖励。
因此计算表格的数值步骤为:
1) Q-table 初始化为 0。
2) 根据当前的 Q-table 给当前状态选择一个动作并执行。执行过程是一直到本轮训练停止才算完成。所谓 ε 贪婪策略是指开始时通过设置一个较大的 ε,让智能体探索环境并随机选择动作。随着智能体对环境的了解,降低 ε,这样智能体开始利用环境做出动作。
当某状态下选择了某个动作后,就可以用 Bellman 方程计算 Q 值:
qπ(st, at)=E[Rt+1+γRt+2+γ2Rt+3+…][st, at]
其中,qπ(st, at) 为给定特定状态下的状态 Q 值;E[Rt+1+γRt+2+γ2Rt+3+…] 为预期折扣累积奖励;[st,at] 为给定状态和动作。3) 评估:采取动作得到了奖励后就可以用 Q 函数更新 Q(s, a),新 Q(s, a)=Q(s, a)+α[R(s, a)+γmaxQ′(s′, a′)-Q(s,a)]
- 新 Q 值作为动作与状态;
- α 作为学习率;
- R(s, a) 为在该状态下采取该动作的奖励;
- Q(s, a) 为当前 Q 值;
- maxQ′(s′, a′) 为给定新状态和在该新状态下的所有可能行动的最大预期未来奖励;
- γ 为折扣率。
【实例】利用 Python 实现 Q-learning 算法。
import pandas as pd
import random
import time
# 参数
epsilon = 0.1 # 贪婪度
alpha = 0.1 # 学习率
gamma = 0.8 # 奖励递减值
# 智能者的状态,即可到达的位置
states = range(6) # 状态集
actions = ['left', 'right'] # 动作集
rewards = [0, 0, 0, 0, 1] # 奖励集
q_table = pd.DataFrame(data=[[0 for_in actions] for_in states], index=states, columns=actions)
def update_env(state):
global states
env = list('-----T')
if state != states[-1]:
env[state] = '0'
print('\r{}'.format(''.join(env)), end='')
def get_next_state(state, action):
'''对状态执行动作后,得到下一状态'''
global states
if action == 'right' and state != states[-1]: # 除非最后一个状态(位置),向右就+1
next_state = state + 1
elif action == 'left' and state != states[0]: # 除非最前一个状态(位置),向左就-1
next_state = state - 1
else:
next_state = state
return next_state
def get_valid_actions(state):
'''取当前状态下的合法动作集合,与奖励无关'''
global actions
valid_actions = set(actions)
if state == states[-1]: # 最后一个状态(位置),则
valid_actions = set(['right']) # 不能向左
if state == states[0]: # 最前一个状态(位置),则
valid_actions = set(['left']) # 不能向右
return list(valid_actions)
for i in range(13):
current_state = 0
update_env(current_state) # 环境相关
total_steps = 0 # 环境相关
while current_state != states[-1]:
# 探索
if random.uniform(0, 1) > epsilon or (q_table.loc[current_state] == 0).all():
current_action = random.choice(get_valid_actions(current_state))
else:
current_action = q_table.loc[current_state].idxmax() # 利用(贪婪)
next_state = get_next_state(current_state, current_action)
next_state_q_values = q_table.loc[next_state, get_valid_actions(next_state)]
q_table.loc[current_state, current_action] += alpha * (
rewards[next_state] + gamma * next_state_q_values.max() - q_table.loc[current_state, current_action])
current_state = next_state
update_env(current_state) # 环境相关
total_steps += 1 # 环境相关
print('\rEpisode {}: total_steps={}'.format(i, total_steps), end='') # 环境相关
time.sleep(2) # 环境相关
print('\r ', end='') # 环境相关
print('\nq_table:')
print(q_table)
运行程序,输出如下:
q_table: left right 0 0.0 0.002646 1 0.0 0.017490 2 0.0 0.085685 3 0.0 0.302924 4 0.0 0.745813 5 0.0 0.000000
 ICP备案:
ICP备案: 公安联网备案:
公安联网备案: